The demand for wireless internet access is constantly rising, supporting people in their daily activities from professional communications to entertainment purposes. However, this increased demand comes with a price – greater power consumption leading to higher carbon emissions. As a result, researchers are now focusing on developing energy-efficient techniques to support communication needs while minimizing power consumption.
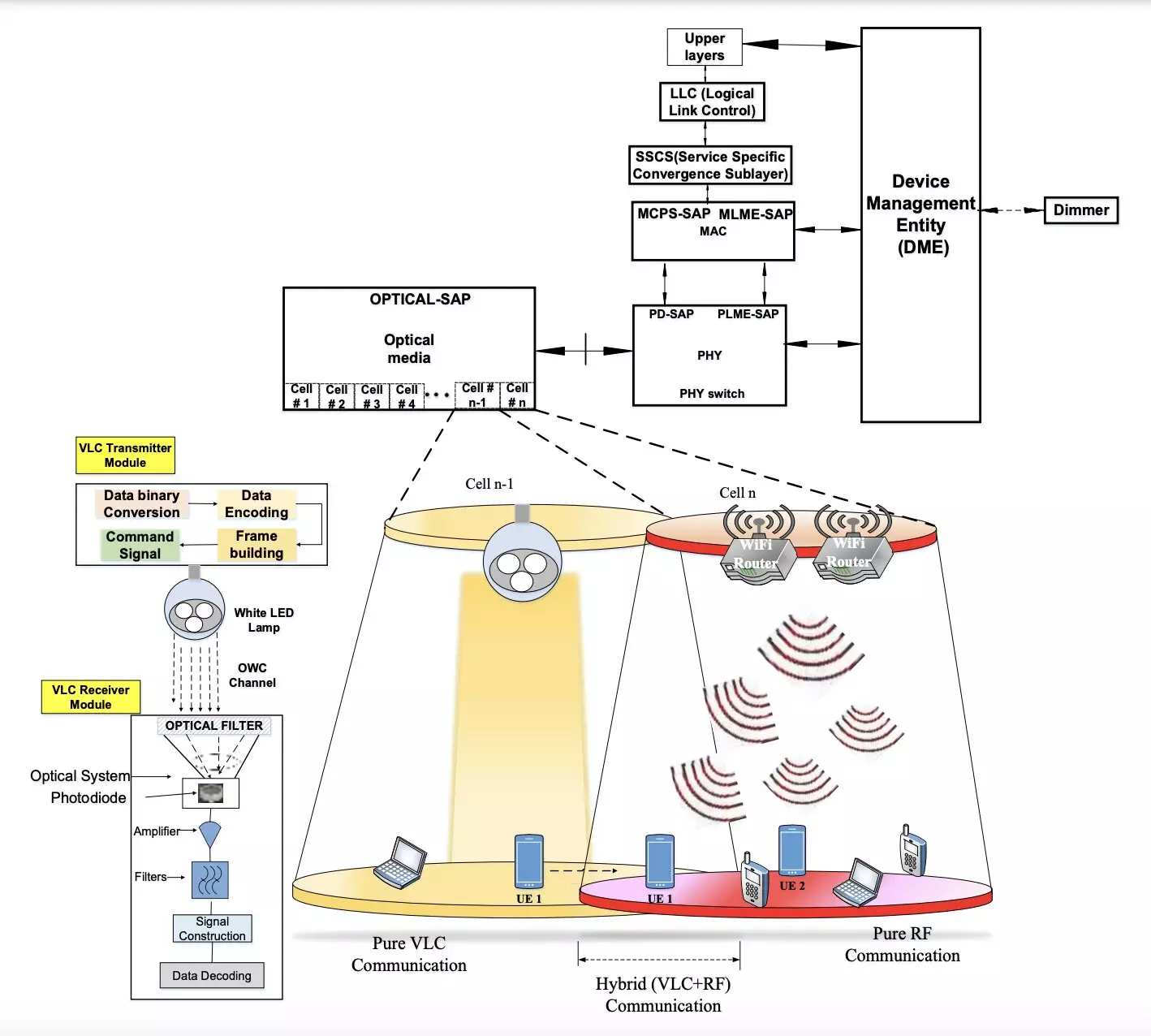
In recent developments, researchers at Central University in India have introduced a new hybrid approach that merges Visible Light Communication (VLC) with Radio Frequency (RF) communication. This innovative solution, as outlined in their paper published in IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, aims to enable reliable communication in indoor environments with a high data transmission rate while consuming less energy.
The Transmitter and Receiver Modules
The wireless communication system devised by the researchers consists of two key components: a transmitter and a receiver module. These modules, although physically separate, are connected via a VLC channel. The transmitter utilizes LED-produced light to transmit binary data, while the receiver, equipped with a photosensitive device like a photodiode or a camera, extracts the transmitted information. This innovative approach ensures a continuous data stream while keeping power consumption at a constant level.
The team of researchers conducted an initial evaluation of their proposed indoor wireless communication system using simulation platforms such as Python, Scilab, and MathWorks tool. Their findings indicate that the system could facilitate stable communication within the same indoor environment while achieving significant energy savings. The proposed hybrid solution not only enhances energy efficiency but also reduces Specific Absorption Rate (SAR), incident power density, and temperature elevation in human tissues exposed to radiation. Moreover, it extends the battery life of mobile devices by approximately 7 hours, as verified by the results obtained from the study.
Future Implications
This recent study by the researchers contributes to the ongoing efforts to reduce power consumption and electromagnetic radiation in wireless communications. The promising results of their initial simulations suggest that the hybrid approach of combining VLC and RF communication could be further enhanced and tested in future studies. By improving energy efficiency and promoting sustainable practices in wireless communication, this hybrid solution could pave the way for a more environmentally friendly and reliable network system.
Overall, the innovative approach of merging VLC with RF communication presents a promising solution to the energy consumption challenges faced by wireless networks. With the continuous advancements in technology and research, the future of wireless communication looks brighter, offering a more efficient and sustainable network for users worldwide.

Leave a Reply