As the global push for renewable energy intensifies, tidal power is emerging as a significant player within the UK’s energy landscape. With a coastline brimming with potential, projections indicate a surge in the number of tidal and offshore renewable installations in the coming decades. However, the inherent challenges posed by the ocean environment—particularly the unpredictable and often turbulent tidal flows—represent a formidable barrier to realizing these ambitious plans.
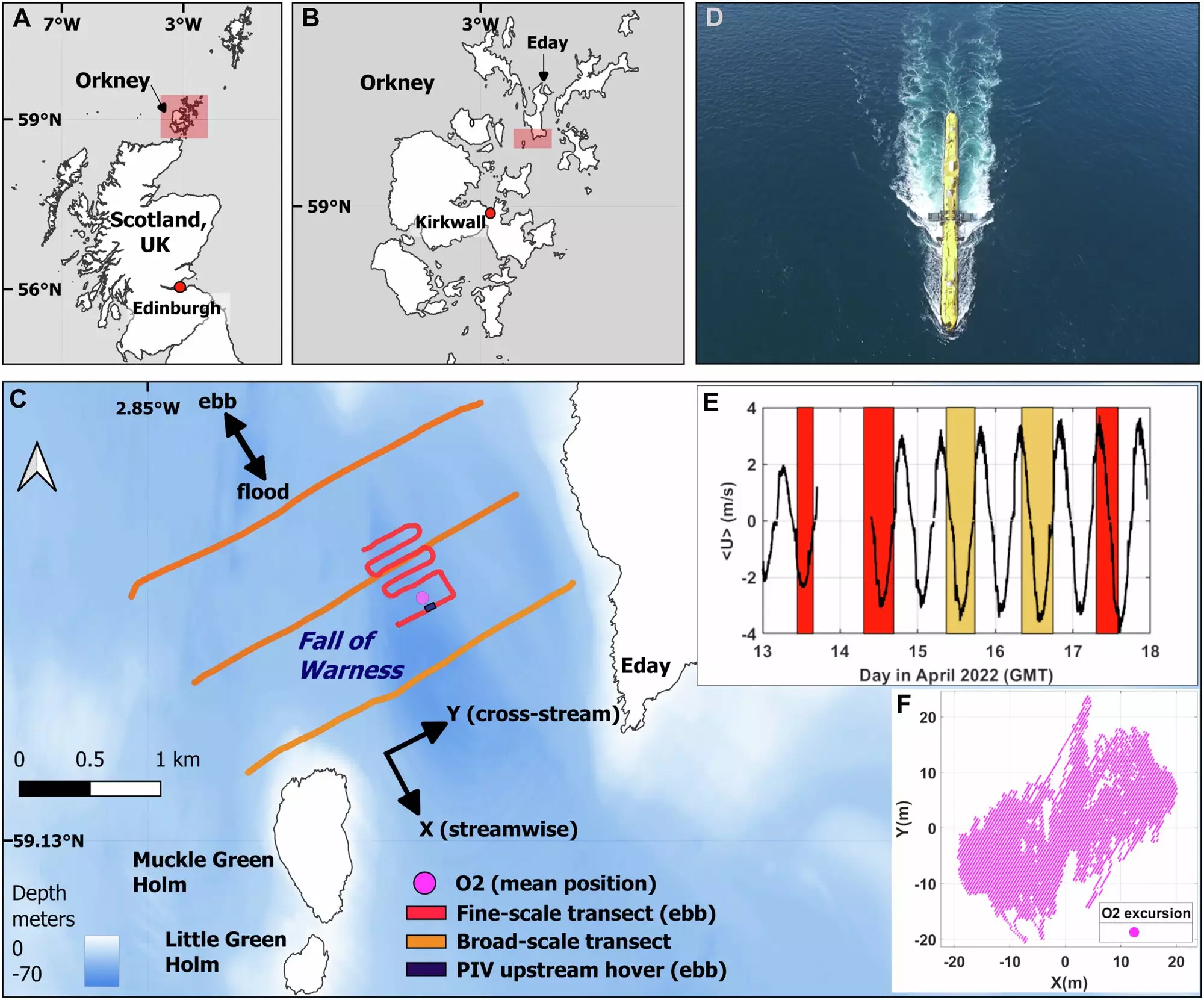
Recognizing these challenges, a research team has embarked on an exploratory mission to assess and map tidal flows, focusing on one of the UK’s most powerful tidal turbines—the O2, developed by Orbital Marine Power. This unique turbine, stationed in Orkney, Scotland, boasts a floating design that sets it apart from conventional underwater turbines. Stretching over 70 meters in length and anchored to the seabed, the O2 is capable of generating enough energy to power around 2,000 homes annually.
Recent studies have provided invaluable insights into how shifting tidal currents—some reaching velocities of over 8 knots—interact with the O2 turbine. Using advanced aerial drone technology paired with traditional boat-based surveys, researchers are identifying optimal placement for tidal turbines. These studies have realigned perspectives on how turbine placement can affect both energy production capabilities and the surrounding marine environment.
The research highlights a crucial aspect of sustainable energy development: understanding how turbine wake can either positively or negatively influence marine ecosystems. The findings suggest potential foraging hotspots created by the turbine’s wake, which are particularly relevant for local seabird populations. While this can foster biodiversity in certain respects, there is also a risk that closely packed turbines could limit the movement of marine species, including fish and mammals.
Intriguingly, during drone surveying, scientists documented orca activity nearby, underscoring the importance of taking marine habitat interactions into account. Such details are vital if developers intend to maximize environmental benefits alongside energy yields, preserving biodiversity while pursuing cleaner energy alternatives.
The collaboration between the Marine Biological Association (MBA), the University of Plymouth, and the University of the Highlands and Islands (UHI) Shetland reflects an interdisciplinary approach that is essential in tackling the complexities of tidal energy. Dr. Lilian Lieber, a senior research fellow, emphasizes the exhilarating yet challenging nature of gathering data in such dynamic environments. This teamwork illustrates how scientific inquiry and technological innovation can coalesce to produce insights crucial for the growth of tidal energy.
Moving forward, the UK could see a particularly promising future for tidal energy. Current assessments predict that tidal stream energy has the potential to contribute up to 11% of the nation’s electricity demands, creating renewable energy avenues that could significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Current Challenges Facing the Tidal Energy Sector
Despite the optimism surrounding tidal energy, the industry must confront numerous hurdles. Among these are the high costs associated with scaling up tidal technologies, challenges regarding grid connectivity, and the technical durability of turbines in harsh conditions. The research team’s innovative field techniques are geared toward addressing these aspects, fostering a robust understanding of tidal dynamics necessary for the reliability and sustainability of tidal energy infrastructure.
Professor Alex Nimmo Smith asserts the critical need for assessments that account for real-world environmental conditions over simulations. He envisions the proliferation of offshore renewable energy platforms across the UK coast, highlighting that the natural ocean conditions vary considerably, complicating replication efforts in controlled environments.
Concluding Thoughts on Tidal Energy’s Promise
As the UK prepares to embrace tidal energy, ongoing research focused on optimizing turbine placement and understanding ecological interactions will be key to balancing energy production with environmental stewardship. The results of this study may serve as a roadmap for similar installations nationwide, catalyzing the migration towards a future powered by clean, renewable energy. The commitment to innovation, as exemplified by the collaboration among researchers, showcases a path forward wherein tidal power not only meets energy needs but also safeguards marine ecosystems in the process. By navigating the complexities of tidal energy development, the UK stands at the forefront of a clean energy revolution poised to make a lasting impact on the energy sector.

Leave a Reply