The evolution of artificial intelligence (AI) has ushered in a new phase of virtual assistance characterized by agentic intelligence. This concept involves AI systems that can take initiative, executing user commands in a way that mimics human decision-making. The current landscape showcases various innovations aimed at streamlining user experiences, especially in fields such as online reservations and personal task management.
Challenges in Restaurant Reservations
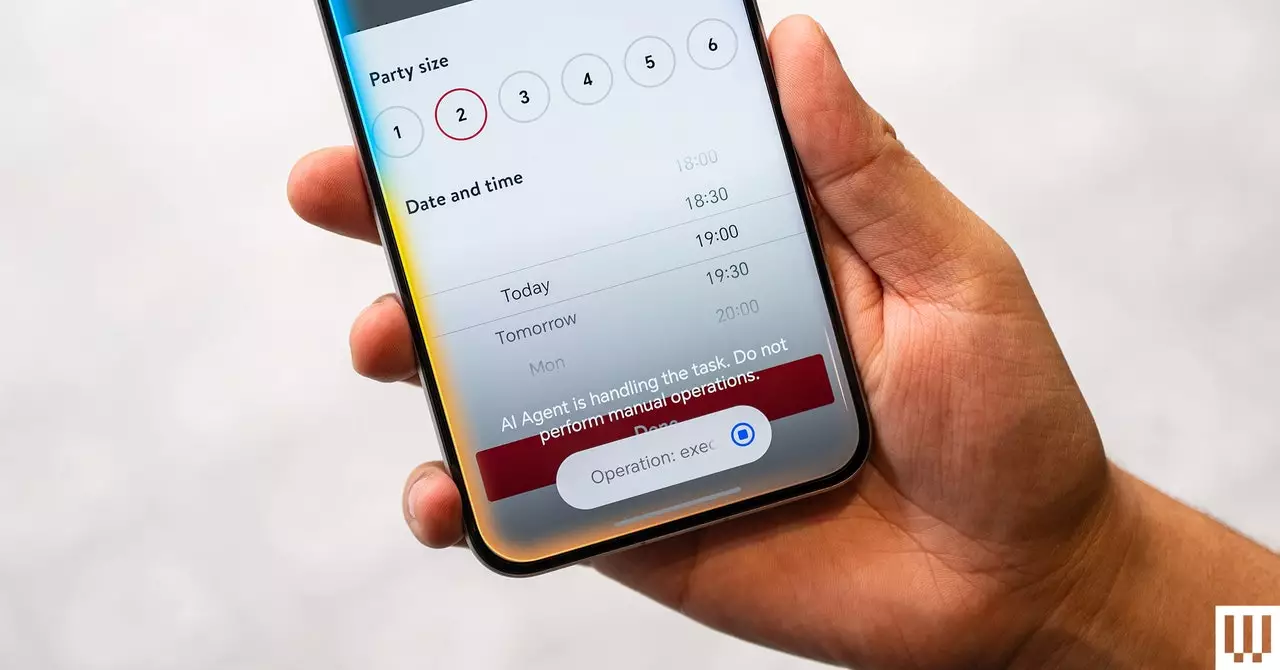
A recent scenario encapsulates the limitations of existing AI capabilities. When a user attempts to reserve a table at a restaurant using an AI assistant, the experience can become cumbersome if the process encounters obstacles, such as requiring a credit card for confirmation. At this juncture, the AI’s ability to facilitate the task falls short as it often requires direct user intervention to complete the process. This gap in functionality highlights the necessity for AI to be not only capable of executing commands but also adept at navigating the associated hurdles autonomously.
Another example underscores the current limitations of AI when tasked with finding a “highly rated” restaurant. While the AI can access and filter reviews based on star ratings, it lacks the depth of analysis required to truly understand the nuances of customer feedback. The absence of cross-referencing capabilities, where the AI would synthesize data from multiple sources, restricts its performance. Furthermore, because much of the AI’s processing occurs on-device without cloud-based support, the breadth of information it can consider is inherently limited. This raises questions about the reliability of such recommendations and the potential for user dissatisfaction.
Emerging Trends in AI Assistance
Despite the limitations, the surge of interest surrounding agentic AI is hard to overlook. Industry leaders, including Google, are making strides with models like Gemini 2, which are designed to act autonomously on behalf of users. This represents a shift towards generative user interfaces, wherein commands are processed in real-time, allowing seamless interaction without the need to open specific applications. This approach, prominently discussed at industry events like Mobile World Congress 2024, suggests a future where user interactions are defined more by conversational AI rather than traditional app-based interfaces.
Honor’s model, akin to the functionalities of Rabbit’s Teach Mode, presents an innovative method for refining AI capabilities. By training the AI manually to complete tasks, users can create a customized experience that aligns with their specific needs. This process eliminates the necessity of traditional APIs, instead allowing the assistant to store and recall processes, which enhances its utility over time. The implications for a more personalized AI experience are profound, fostering deeper user engagement and satisfaction.
While agentic AI is a compelling concept, its current practical applications reveal both promise and limitation. As technology progresses, the ability of AI to independently navigate complex tasks will undoubtedly improve, offering more seamless and satisfying user experiences. As we embark on this journey, it’s crucial for developers to address existing shortcomings while pushing the boundaries of what AI can achieve. The future of virtual assistance promises a revolution in how we interact with technology, making it an exciting avenue to watch.

Leave a Reply