Researchers at the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Huazhong University of Science and Technology, have introduced a groundbreaking electrochromic (EC) structure for energy-saving windows. This innovative technology has the potential to significantly reduce the energy consumption of buildings by dynamically regulating solar radiation through external voltage stimuli. While previous efforts have focused on enhancing EC performance, such as response speed and contrast ratio, there has been limited success in mitigating the impact of solar radiation and outdoor temperature fluctuations.
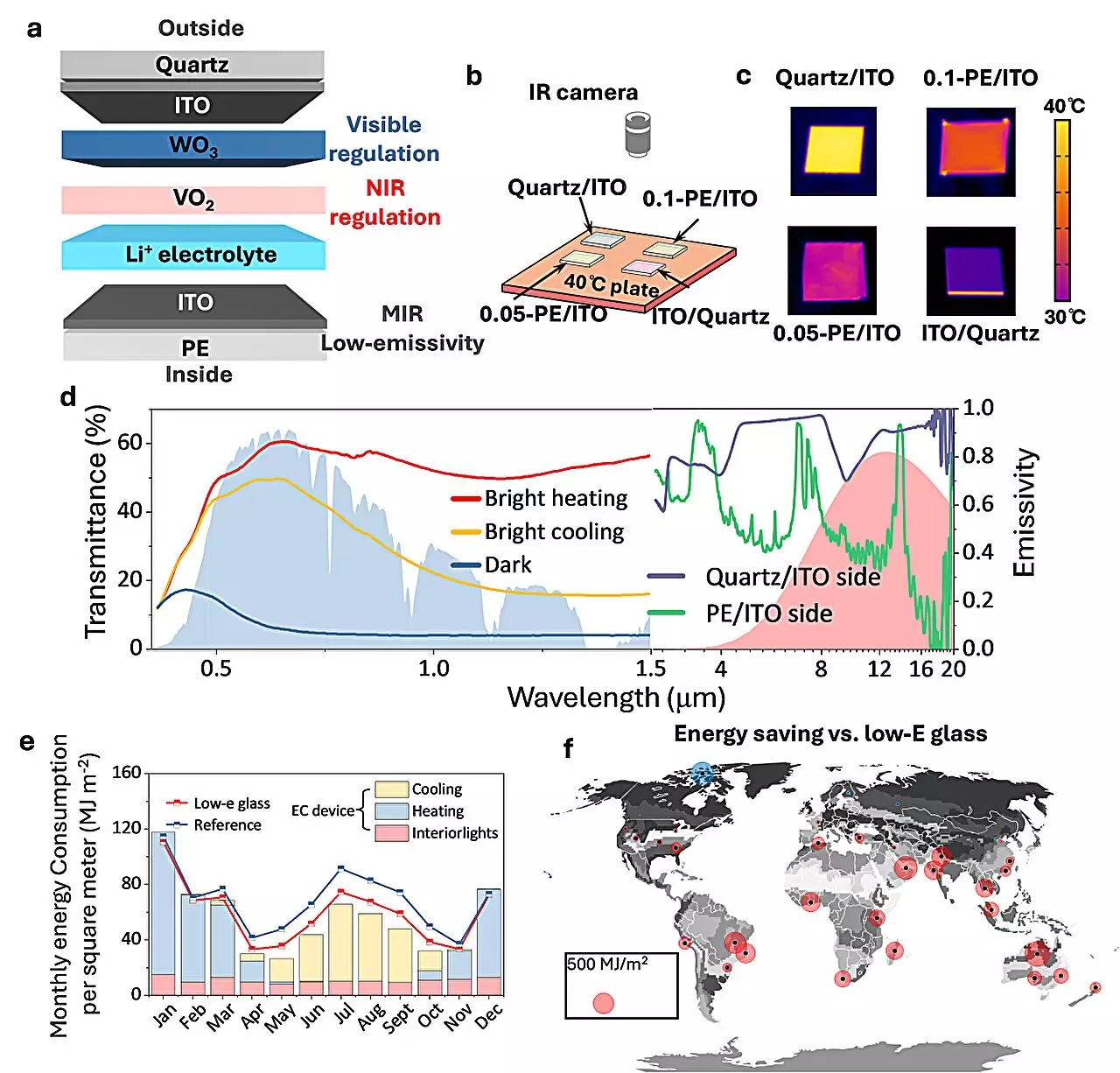
The team devised a novel electrochromic smart window system utilizing a VO2-WO3 tandem film within a solid electrolyte. This design enables the tri-stable control of solar heat and sunlight transmittance concurrently, resulting in substantial energy savings. By allowing Li+ diffusion along the depths of VO2 and WO3, the system can independently adjust the near-infrared (NIR) and visible transmittance of sunlight. One key advantage of VO2 is its ability to decouple the barrier for maintaining the state from the barrier for changing the state, ensuring non-volatility compared to WO3.
Energy-efficient Operation
The new EC-based windows demonstrate superior performance in minimizing the total energy cost of indoor lighting and heat exchange, making them an ideal choice for smart window design. Simulations indicate that this innovative technology outperforms commercial low-E glass in terms of heating and cooling energy savings across various climates worldwide. Outdoor experiments conducted in Sanya, Hainan Province, and Shanghai have shown consistent cooling of up to 2°C–14°C throughout a typical clear sunny day.
The development of this advanced electrochromic smart window system opens up new possibilities for energy-efficient building design and sustainability initiatives. By harnessing the power of cutting-edge materials and innovative technologies, researchers are paving the way for a more environmentally friendly and cost-effective approach to energy consumption in the construction sector. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change and resource depletion, breakthroughs like these offer a glimmer of hope for a brighter and more sustainable future.

Leave a Reply