The field of robotics stands on the brink of a sensory revolution, thanks to groundbreaking research from the German Aerospace Center’s Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics. By merging traditional internal force-torque sensors with advanced machine-learning algorithms, researchers are redefining how robots sense and react to touch. This innovative approach veers away from the conventional use of artificial skin, presenting a more sophisticated and efficient method for robots to understand tactile interactions.
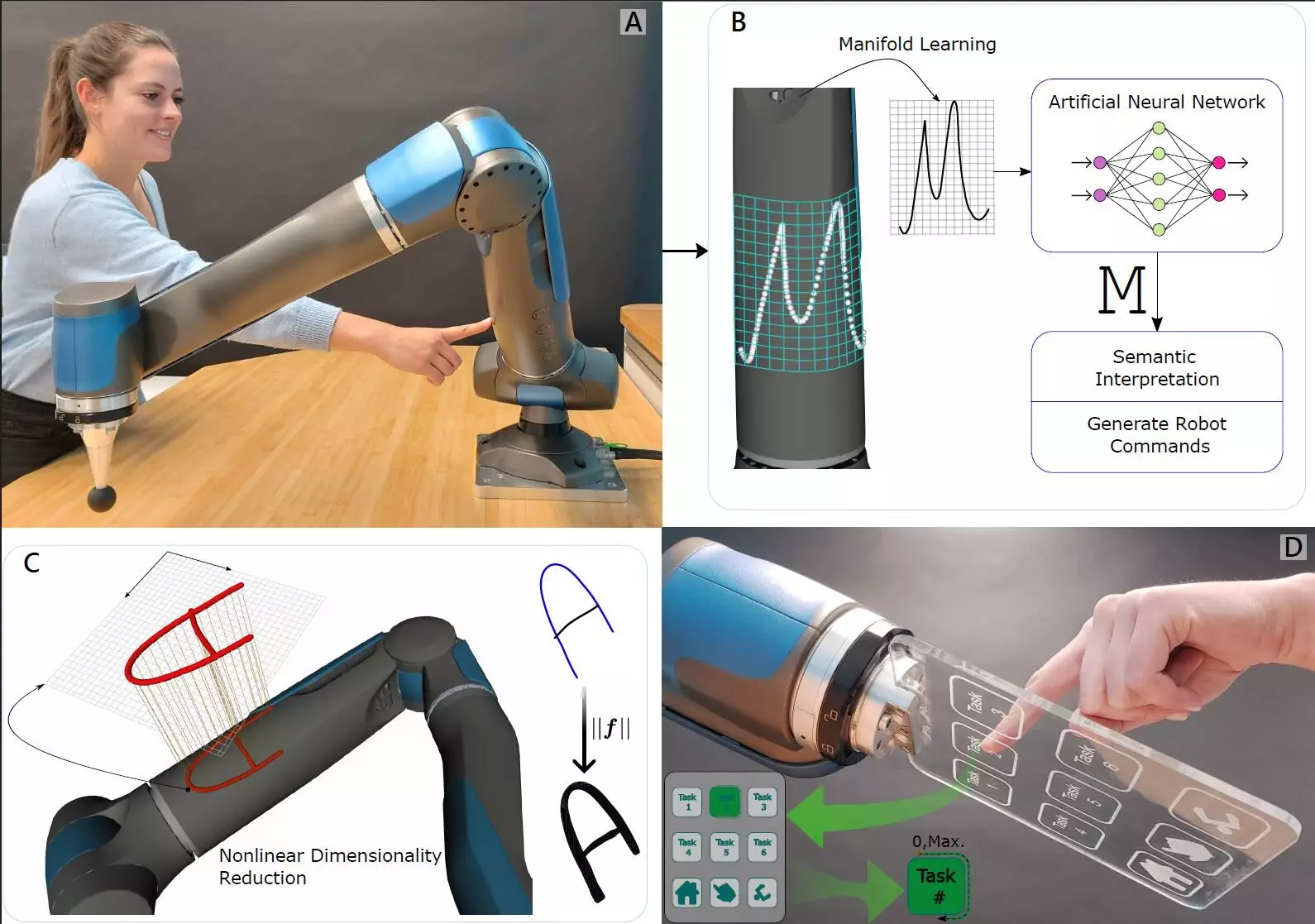
Touch, a fundamental sense for living organisms, is a complex interplay of sensations, allowing us to perceive texture, temperature, and pressure. In the robotic realm, replicating this intricate experience has often been an elusive goal. However, the research team’s ingenious strategy sheds light on overcoming this barrier. They discovered that the mechanics of touch could be effectively simulated in robots through the understanding of torque and tension. By embedding ultra-sensitive force-torque sensors in robot joints, they created a platform where robots can intelligently respond to external stimuli, mimicking the intricacies of biological touch.
Deciphering the Language of Touch
A pivotal aspect of this research is how the robot interprets various tactile inputs. The internal sensors not only detect but also analyze the pressure exerted from myriad directions, opening the door for a form of sensory intelligence that closely mirrors human touch processing. Machine learning plays a crucial role in teaching the robot to differentiate and categorize the types of pressures it experiences. This ability to “learn” from touch is reminiscent of how humans develop tactile sensitivity over time through experience.
The team’s findings revealed remarkable capabilities; the robot could distinguish between specific points of contact along its arm as well as recognize numbers pressed against it—a feat that highlights the advanced potential of this new tactile sensing mechanism. Such capabilities dramatically enhance the operational effectiveness of robots, particularly in environments where delicate interactions with human counterparts are necessary.
Implications for Human-Robot Collaboration
The ramifications of this technological advancement extend far beyond mere academic interest; they herald a future where robots can seamlessly integrate into human workspaces. The heightened sensitivity achieved through this method could redefine roles in industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare, where close human-robot interaction is becoming increasingly prevalent. As robots evolve to understand touch in a more human-like manner, they can become more intuitive collaborators, responding to human cues in a natural and effective way.
Moreover, the absence of artificial skin—often cumbersome and prone to wear—means that these robots will require less maintenance and offer increased durability. As such, this innovation is poised to enhance not only efficiency and safety in human-robot interactions but also to enrich the quality of collaboration that can take place.
The fusion of force-torque sensors with machine learning does not just represent a leap forward in tactile robotics; it symbolizes a fundamental shift in how we envision the capabilities of machines in our daily lives. With this newfound awareness of touch, the possibilities are infinite, suggesting a future where technology and humanity blend harmoniously in unprecedented ways.

Leave a Reply