Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with researchers at Central China Normal University, have made a significant stride in the field of medical imaging. Their groundbreaking research, recently published in Nature Communications, introduces a high-performance perovskite X-ray complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) detector that promises to revolutionize the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular and cancer diseases.
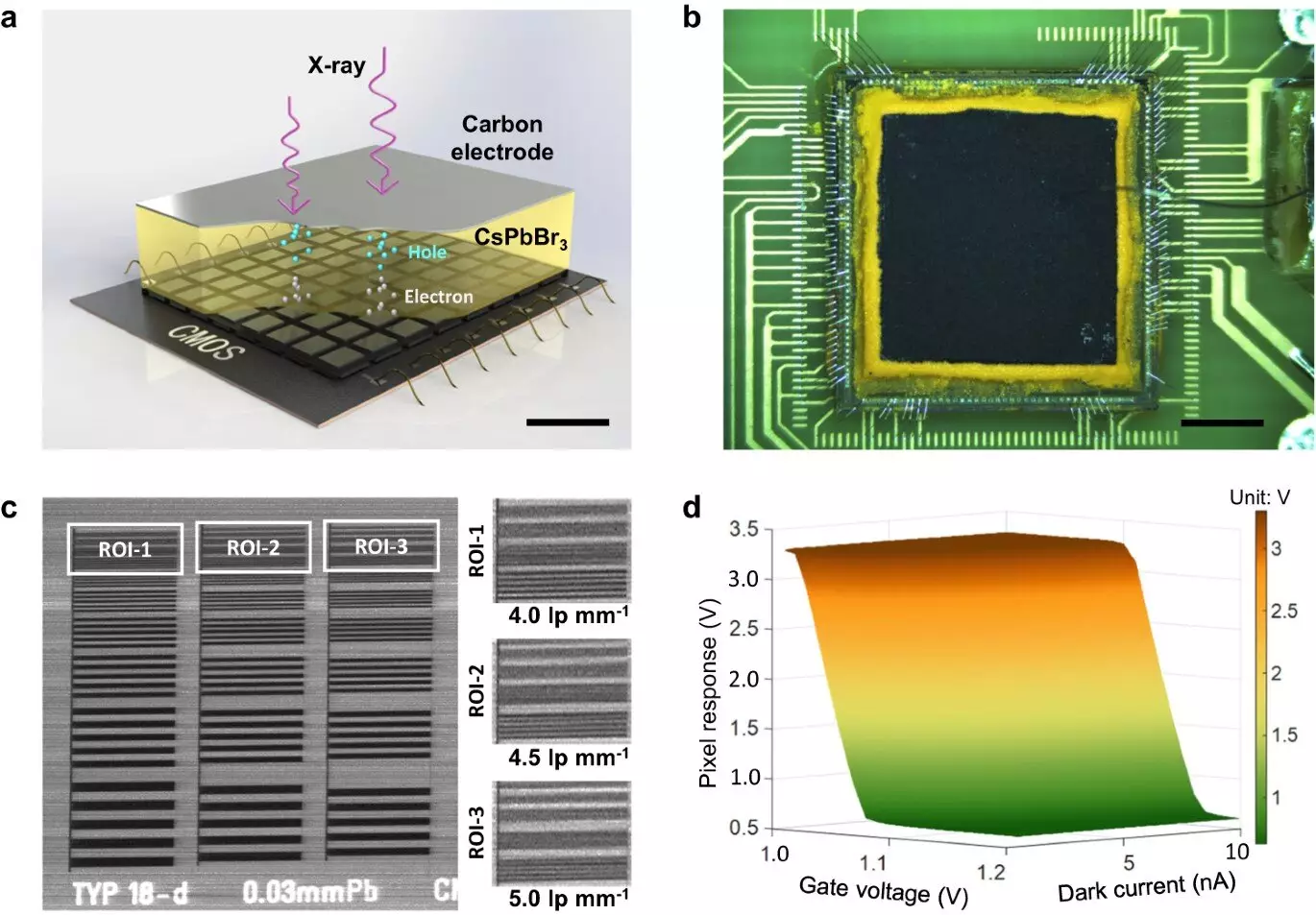
Traditional X-ray detectors made of semiconductor materials like Si, a-Se, and CdZnTe/CdTe have certain limitations that hinder their effectiveness in general X-ray imaging. These materials either have low X-ray absorption efficiency or are prohibitively expensive. Perovskite, on the other hand, offers a viable alternative with its unique properties. The study explores the integration of perovskite, specifically a 300 μm thick inorganic CsPbBr3 film, with a dedicated CMOS pixel array to create a direct-conversion X-ray detector.
The direct-conversion X-ray detector developed by the researchers showcases exceptional performance metrics. The CsPbBr3 perovskite film boasts a high μτ product, a measure of charge carrier mobility, as well as an impressive X-ray detection sensitivity and a low dose detection limit. The experimental results demonstrate the remarkable spatial resolution and low-dose imaging capabilities of the perovskite CMOS detector, surpassing the hardware limits of conventional detectors.
The successful demonstration of lead halide perovskites in X-ray detector technology opens up new possibilities for enhancing the spatial resolution, readout speed, and dose detection efficiency in medical imaging. Prof. Ge, the lead researcher, highlights the transformative potential of perovskite materials in driving the development of state-of-the-art X-ray detectors. The integration of perovskite technology with CMOS arrays represents a significant step towards achieving superior performance in medical diagnostics and treatment.
The collaborative efforts between SIAT and Central China Normal University have yielded a game-changing advancement in X-ray detector technology. The fusion of perovskite materials with CMOS arrays paves the way for next-generation imaging systems that offer unparalleled resolution, speed, and efficiency. This research not only showcases the capabilities of perovskite technology but also underscores the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in pushing the boundaries of scientific innovation.

Leave a Reply