A recent project conducted by a team of physicists and engineers in China has resulted in the creation of a revolutionary gravimeter. Unlike traditional gravity measurement devices, this new gravimeter is small, highly sensitive, and capable of operating at room temperature. The team’s innovative approach involved the use of a dual magnet strategy combined with laser technology to measure changes in gravity.
Overcoming Existing Drawbacks
Existing gravity measurement devices have been plagued by various drawbacks. For instance, devices based on small oscillators tend to deteriorate quickly, leading to a loss of precision over time. On the other hand, devices relying on superconducting materials require cold containers, making them power-intensive and difficult to transport. The new gravimeter developed by the Chinese research team aims to address these limitations.
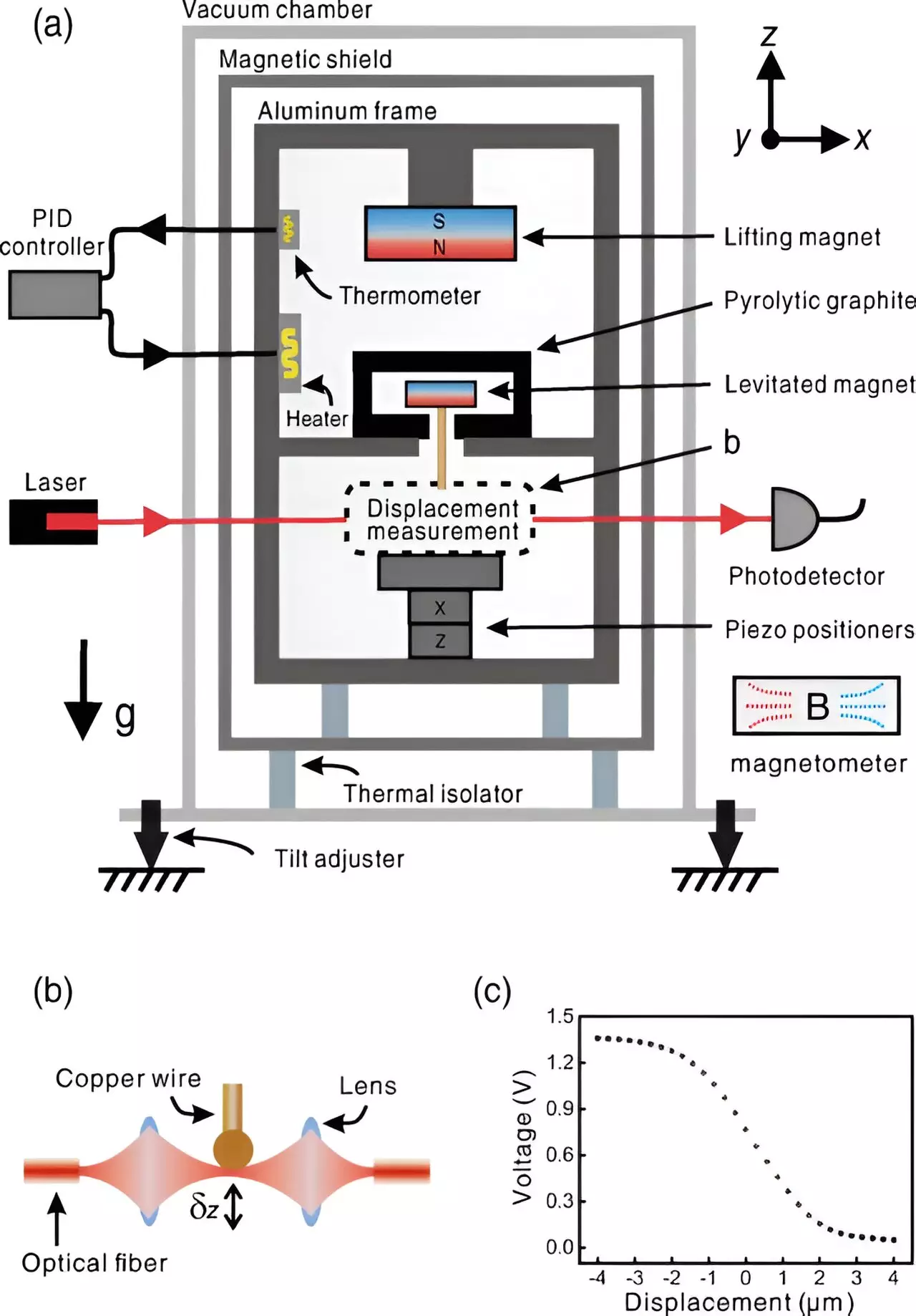
The gravimeter consists of a large magnet housed within a cabinet, along with a smaller magnet positioned beneath it in a field-repelling graphite shell. The opposing magnetism causes the smaller magnet to levitate, resulting in vertical oscillations. By adjusting the spacing between the magnets, the team was able to achieve oscillations of just 1 Hz. A wire hanging down from the larger magnet was used to measure changes in gravitational pull, with its movement being detected by a vertical laser.
Testing and Results
To test the effectiveness of their device, the research team placed it in a vacuum chamber for several weeks to allow for calibration. Subsequently, they conducted measurements of gravity from the moon and sun over a five-day period. Comparing the results with predicted values, the team observed oscillations indicative of variations in gravitational acceleration. These fluctuations were found to be highly accurate, demonstrating the precision of the new gravimeter.
The team regards their work as a proof-of-concept, with potential for further refinement and enhancement. Future iterations of the device are expected to be more physically robust, enabling easy transportation between different locations. The researchers anticipate that ongoing development efforts will lead to even greater precision in gravity measurement, opening up new possibilities for scientific research and exploration.

Leave a Reply