The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) is currently undergoing a substantial upgrade to cater to the increasing needs for high-precision positioning in various industries. The goal of the new services is to provide decimeter-level accuracy in just a matter of minutes, a significant improvement from its current capabilities. This enhancement has become imperative due to the rising dependence on precise location data for the successful operation of technologies like autonomous driving, robotic navigation, and smart city infrastructures.
While systems like the Global Positioning System (GPS), GLObal NAvigation Satellite System (GLONASS), and Galileo have set high standards in the field, challenges such as limited regional coverage and long convergence times still persist. These shortcomings highlight the urgent need for enhanced navigation satellite systems to bridge the existing gaps. The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) aims to tackle these challenges head-on by bolstering its high-precision services, positioning itself as a key player in the realm of global positioning.
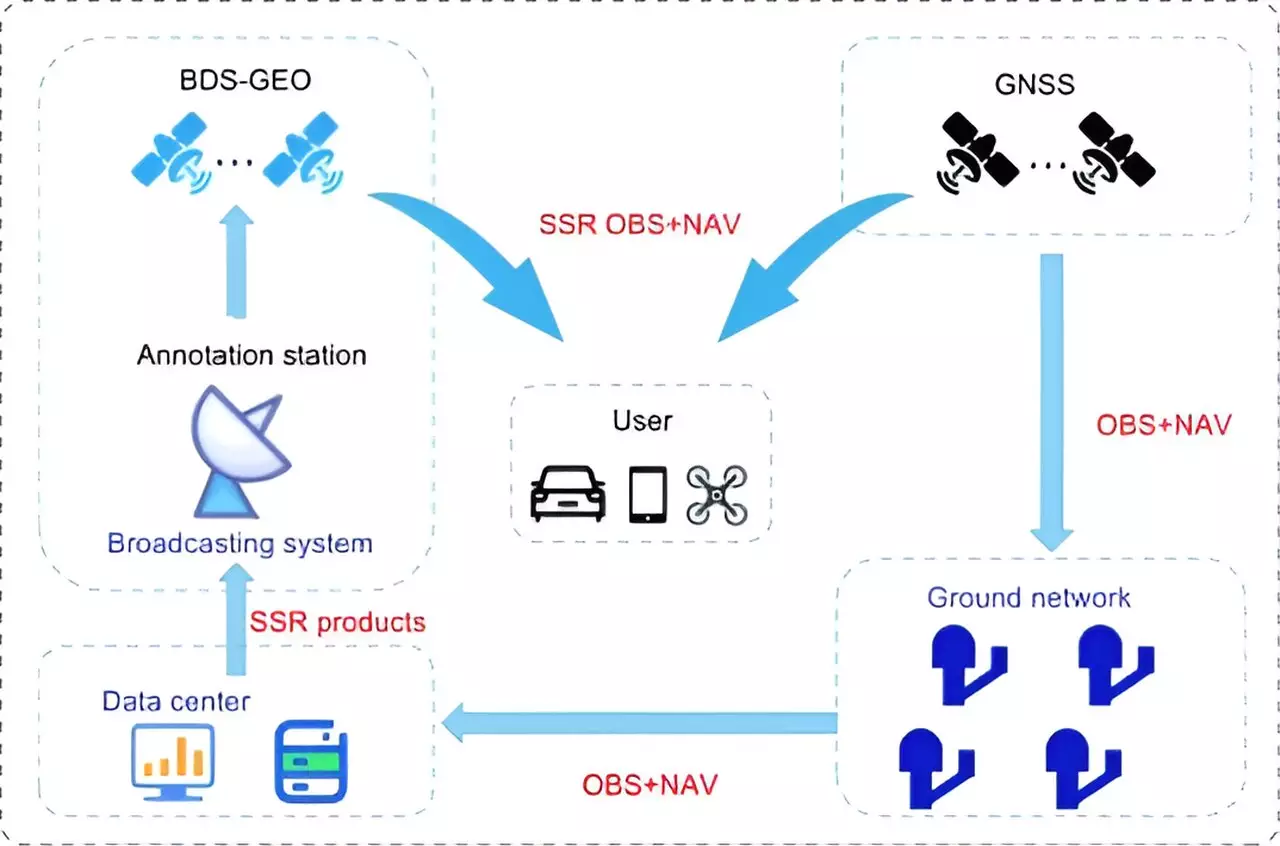
A recent study conducted by researchers from the Beijing Institute of Tracking and Telecommunication Technology, in collaboration with the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory and Wuhan University, sheds light on the current state, achievements, and future trajectory of the BeiDou system’s high-precision services. The study, published in the journal Satellite Navigation on 24 June 2024, specifically delves into the PPP-B2b of BDS-3, which enables decimeter-level accuracy within 14 minutes. However, despite these advancements, BDS-3 still falls short compared to international counterparts like Galileo’s High Accuracy Service (HAS) and Quasi-Zenith Satellite System’s (QZSS’s) Centimeter-Level Augmentation Service (CLAS) in terms of regional coverage and convergence time.
To address the existing limitations, the research suggests a multi-layer development framework that focuses on integrating low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites into the BeiDou system. The incorporation of a LEO constellation consisting of 288 satellites has the potential to enhance positioning accuracy to a level better than 5 cm within approximately 1 minute. This integration not only improves global coverage but also significantly reduces convergence time, enabling rapid and precise positioning capabilities. The simulation results highlight the effectiveness of LEO-enhanced PPP services in overcoming current constraints and solidifying BeiDou’s position as a frontrunner in high-precision satellite navigation.
Dr. Xingxing Li from Wuhan University emphasized the pivotal role of BeiDou’s high-precision services in meeting the escalating demands of modern navigation applications. The incorporation of LEO satellites stands out as a particularly promising development, as it enhances coverage and reduces convergence time significantly. This progress brings us closer to achieving real-time, centimeter-level positioning accuracy on a global scale, marking a significant milestone in the evolution of global navigation satellite systems. The enhanced high-precision services offered by BeiDou have far-reaching implications for various applications, including autonomous driving, unmanned aerial vehicles, and smart device navigation, cementing its status as a leader in this domain.

Leave a Reply