Excitons, the microscopic particle-like objects that are critical to the study of materials known as van der Waals magnets, have been the subject of intense research at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory. The recent findings shed light on the formation and behavior of excitons in nickel phosphorus trisulfide (NiPS3), providing valuable insights into the optical and magnetic properties of these intriguing materials.
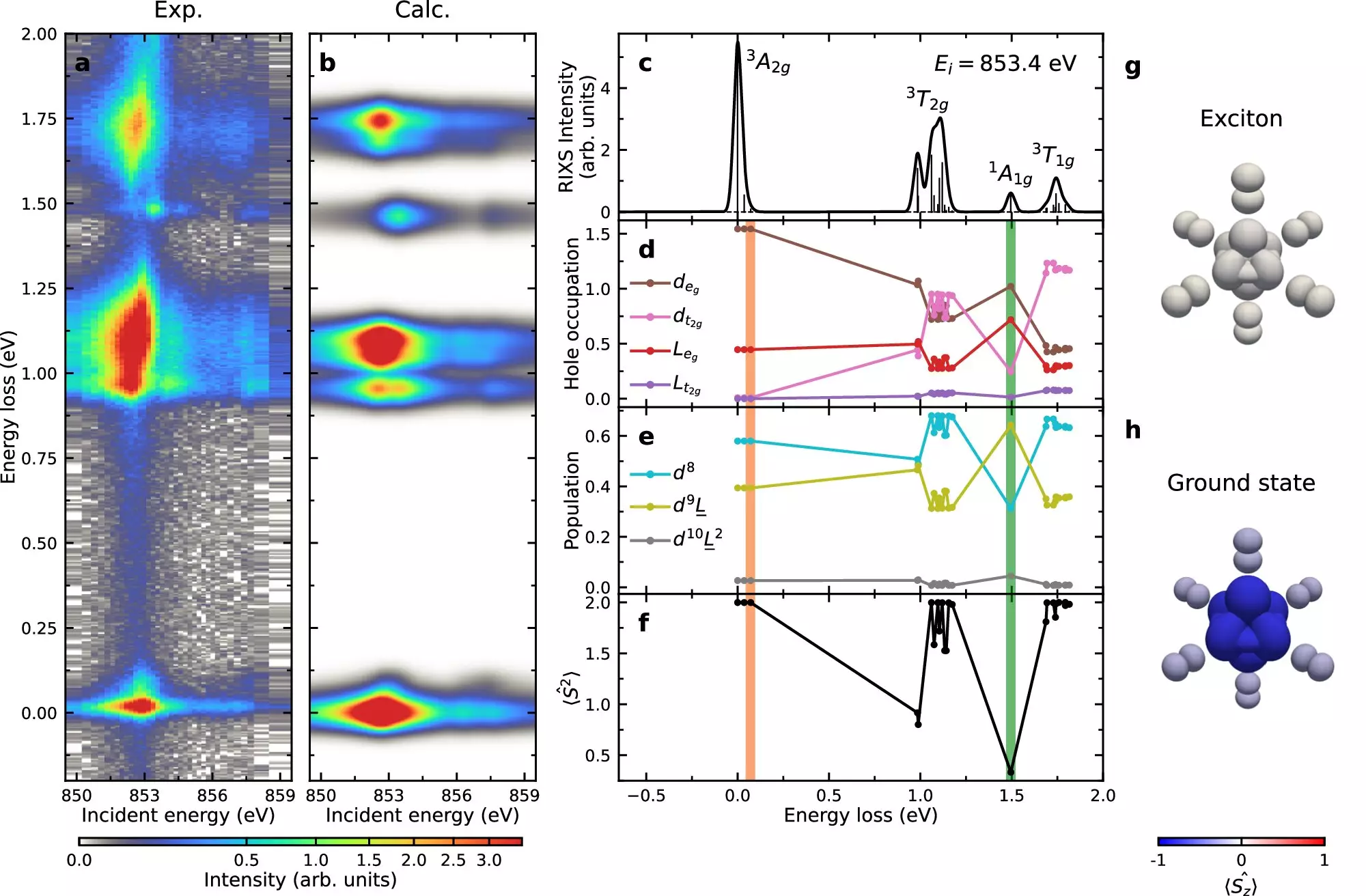
Despite the significant interest in excitons in NiPS3, scientists have struggled to decipher their structure and motion. The research group at Brookhaven tackled this challenge by employing an advanced X-ray technique called resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) at the Soft Inelastic X-ray Scattering (SIX) beamline of the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II). This cutting-edge experimental station allowed the researchers to study the electronic properties of NiPS3 with unparalleled precision, offering a glimpse into the fundamental nature of excitons.
One of the key findings of the study was the crucial role played by the Hund’s exchange interaction in governing exciton formation and propagation in NiPS3. This physics principle determines the energy of different electron spin configurations, providing the necessary energy for excitons to emerge in the material. The researchers also observed that the exciton disperses through the crystal in a manner reminiscent of a double-magnon, highlighting the intricate relationship between excitons and other quasiparticles like magnons in van der Waals magnets.
As the study of excitons in NiPS3 continues to evolve, the researchers anticipate further advancements in instrumentation and techniques like RIXS and electron microscopy. These developments hold the promise of even better measurements of exciton behavior in van der Waals magnets, paving the way for the potential development of new technologies based on magnetism, such as innovative information storage devices. Postdoctoral researcher Wei He, the first author of the study, expressed optimism about the future of exciton research and its implications for future technological breakthroughs.
The exploration of excitons in van der Waals magnets represents a fascinating frontier in materials science, offering unprecedented insights into the interplay between optical and magnetic properties. The recent findings at Brookhaven National Laboratory mark a significant step towards unraveling the mysteries of excitons in nickel phosphorus trisulfide and pave the way for exciting advancements in the field of magnetism-based technologies.

Leave a Reply