In a groundbreaking development within the realm of quantum technology, researchers have achieved a significant milestone in utilizing the frequency dimension in integrated photonics. This advancement not only promises to revolutionize quantum computing but also establishes the foundation for ultra-secure communication networks. Integrated photonics, which involves manipulating light within small circuits on silicon chips, has long been recognized for its potential in quantum applications due to its scalability and compatibility with existing telecommunications infrastructure.
Innovative Silicon Ring Resonators
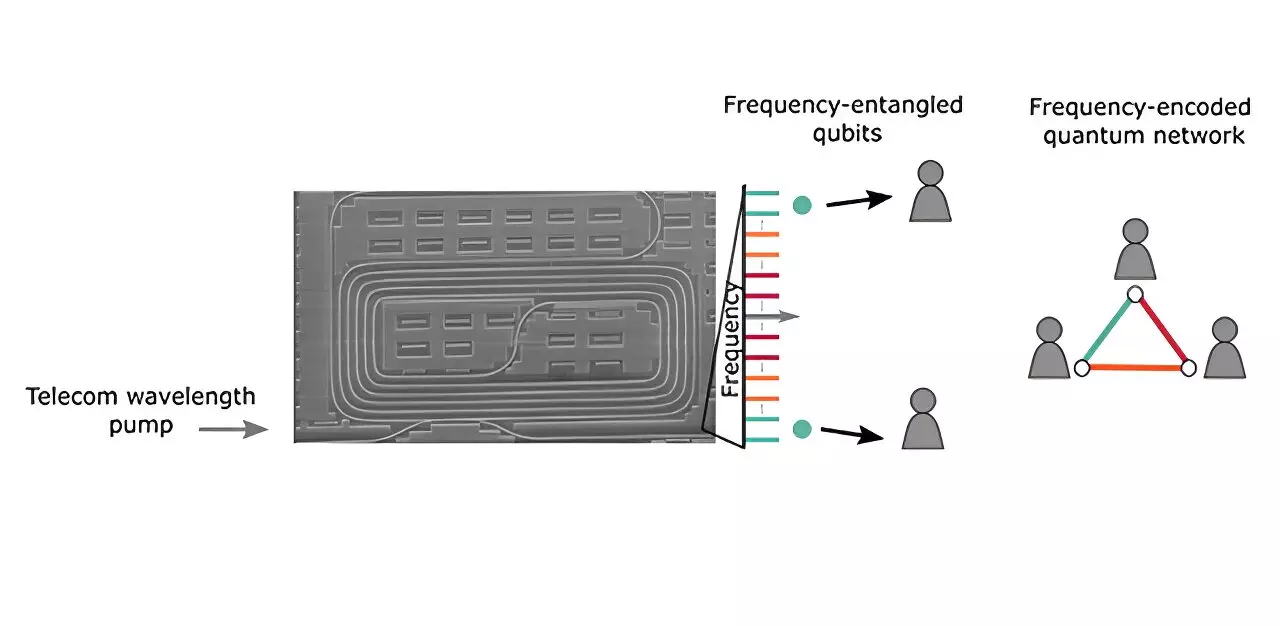
The recent study published in Advanced Photonics by researchers from the Centre for Nanosciences and Nanotechnology (C2N), Télécom Paris, and STMicroelectronics (STM) showcases a major breakthrough. The team has successfully developed silicon ring resonators with a remarkably small footprint of less than 0.05 mm2. These resonators are capable of generating over 70 distinct frequency channels, each spaced 21 GHz apart. This advancement enables the parallelization and independent control of 34 single qubit-gates using only three standard electro-optic devices.
Advanced Quantum State Control
Utilizing these silicon ring resonators, researchers have achieved a critical milestone in creating and controlling quantum states. Through the process of spontaneous four-wave mixing, the team has efficiently generated frequency-bin entangled photon pairs. This capability is essential for constructing quantum networks and quantum circuits. By exploiting narrow frequency separations, the researchers have demonstrated their ability to manipulate and control quantum states with precision.
What sets this research apart is its practicality and scalability. By leveraging the precise control provided by the silicon resonators, the team has demonstrated the simultaneous operation of 34 single qubit-gates using just three off-the-shelf electro-optic devices. This breakthrough paves the way for the development of complex quantum networks where multiple qubits can be manipulated independently and in parallel. Experimental validations at C2N have confirmed the fidelity and coherence of the quantum states, marking a significant advancement towards practical quantum computing.
One of the most noteworthy achievements of this research is the establishment of the first fully connected five-user quantum network in the frequency domain. This accomplishment opens up new possibilities for quantum communication protocols, which rely on secure transmission of information encoded in quantum states. Looking ahead, this research not only highlights the potential of silicon photonics in advancing quantum technologies but also sets the stage for applications in quantum computing and secure communications.
As quantum technologies continue to progress, the utilization of integrated photonics platforms holds the promise of revolutionizing industries that depend on secure data transmission. The ability to leverage the frequency dimension in integrated photonics offers advantages such as scalability, noise resilience, parallelization, and compatibility with existing telecom multiplexing techniques. This significant milestone reported by C2N, Telecom Paris, and STM researchers serves as a guiding light towards a future where quantum networks can offer secure communication solutions.
The fusion of integrated photonics and quantum technology represents a significant step forward in the field of quantum communications. The ability to harness the frequency dimension opens up new possibilities for scalable and efficient quantum networks. With ongoing advancements and innovations in this area, the future of quantum technology appears promising, with vast implications for industries seeking enhanced data security and computational power.

Leave a Reply