Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) have revolutionized gaming and entertainment, but there is still room for improvement. Current technologies mainly focus on visual and auditory sensations, neglecting the crucial sense of touch. However, researchers at City University of Hong Kong and other Chinese institutes are pioneering new haptic interfaces that can simulate realistic tactile sensations directly on the skin, enhancing the immersive experiences offered by VR and AR.
The Need for Tactile Feedback
While existing VR technologies provide captivating visuals and sound, the absence of tactile feedback limits the overall realism of virtual experiences. Based on this recognition, Professor Xinge Yu, alongside his research group at the City University of Hong Kong, has been developing haptic interfaces using flexible electronics. Their previous work introduced a wireless electrostimulation haptic interface, but it primarily focused on creating haptic feedback rather than generating diverse tactile sensations.
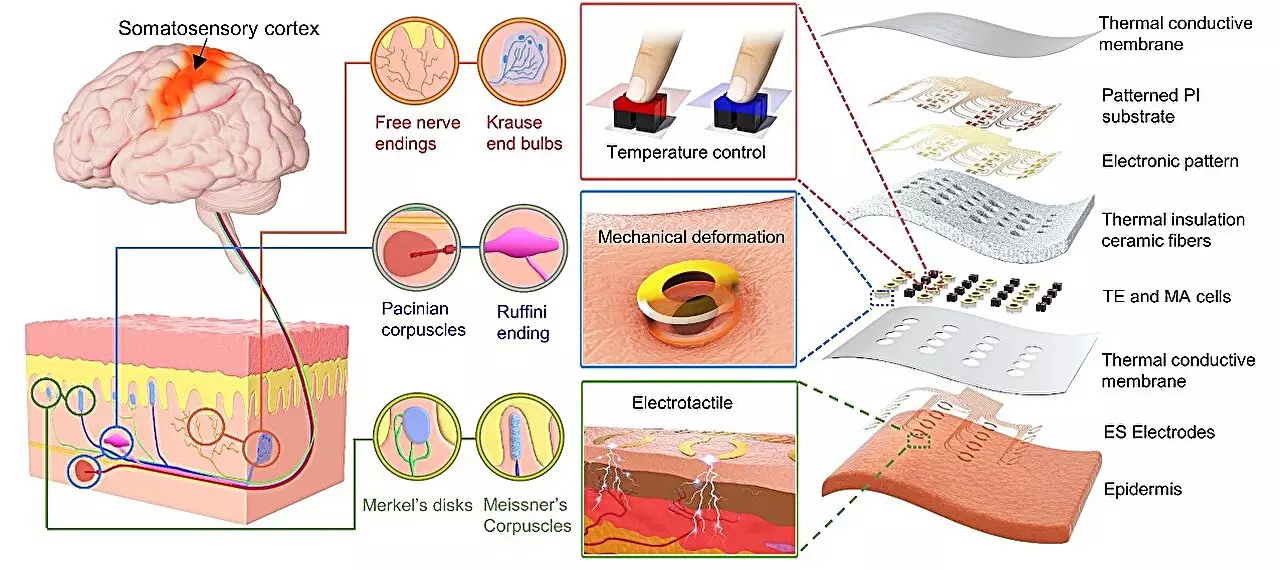
The human body can perceive an extensive range of tactile information when encountering different surfaces and objects. To replicate this capability, the research group at the City University of Hong Kong introduced a new activation principle for their haptic system. By selectively stimulating different sensory receptors, their device can reproduce various tactile sensations corresponding to different textures. This breakthrough could bridge the gap in haptic feedback generation and revolutionize the VR and AR industry.
Current haptic feedback technologies fall into two main categories: electrical stimulation and mechanical actuation. Electrical stimulation focuses on accurately activating nerves to generate realistic tactile sensations within the human body. On the other hand, mechanical actuation aims to mimic tactile experiences by designing interactive interfaces or devices that replicate the skin’s surface deformation when interacting with real objects. Both approaches have their challenges, but the researchers at City University of Hong Kong have successfully combined the advantages of both methods, resulting in more diverse and immersive tactile feedback effects.
Through their innovative approach, the research team has broken down the barriers that previously separated electrical stimulation and mechanical actuation in haptic feedback generation. By selectively stimulating touch receptors based on the distribution rules within the human body, they have created a skin-integrated multimodal haptic interface. This integration of multiple feedback modes within a single device opens up new possibilities for providing users with richer and more realistic touch experiences.
The development of the skin-integrated multimodal haptic interface is a significant contribution to the field of haptic technology. In the future, this breakthrough could lead to highly immersive VR content accompanied by lifelike tactile sensations. However, there is still much work to be done in the field of haptic feedback. Material synthesis, mechanical structure optimization, and neuro electrophysiology are areas that require further research and development for the improvement of haptic interfaces.
The integration of touch sensations into virtual and augmented reality experiences has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with digital environments. The research conducted at the City University of Hong Kong has paved the way for achieving immersive tactile feedback through their skin-integrated multimodal haptic interface. By combining electrical stimulation and mechanical actuation, their innovative approach breaks down previous limitations and opens up new possibilities in the field of haptic feedback. As technology continues to advance, we can look forward to truly immersive virtual experiences that engage the senses in a holistic manner.

Leave a Reply